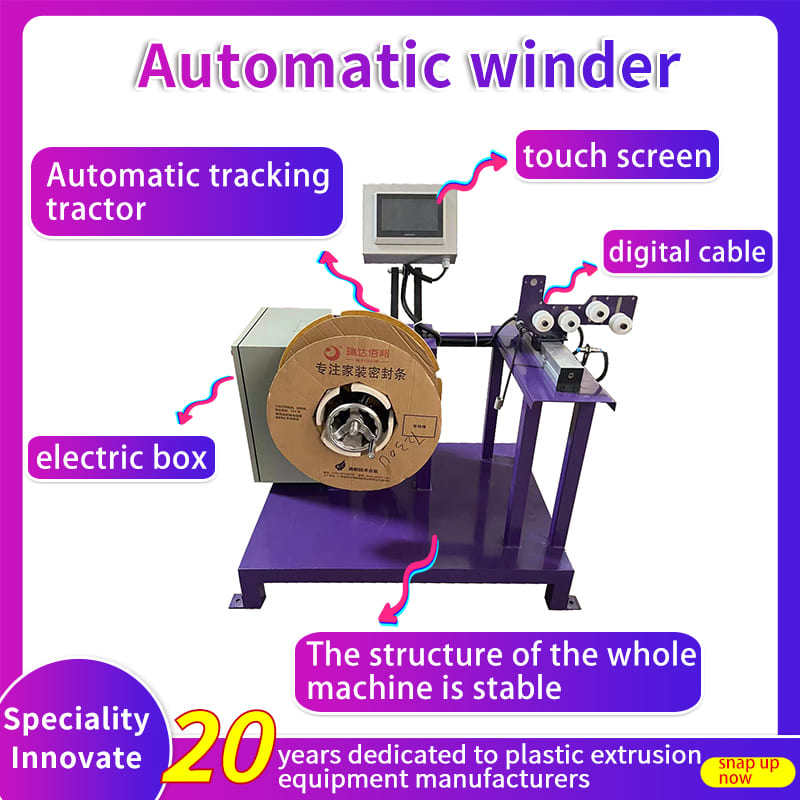
Applications of Automatic Winding Machines in Modern Manufacturing
The advent of automation has revolutionized various sectors of modern manufacturing, and one of the key technologies driving this transformation is the automatic winding machine. These machines have evolved significantly from their manual counterparts, offering enhanced efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness across diverse industries. This article delves into the applications, benefits, and future prospects of automatic winding machines in modern manufacturing.
Introduction to Automatic Winding Machines
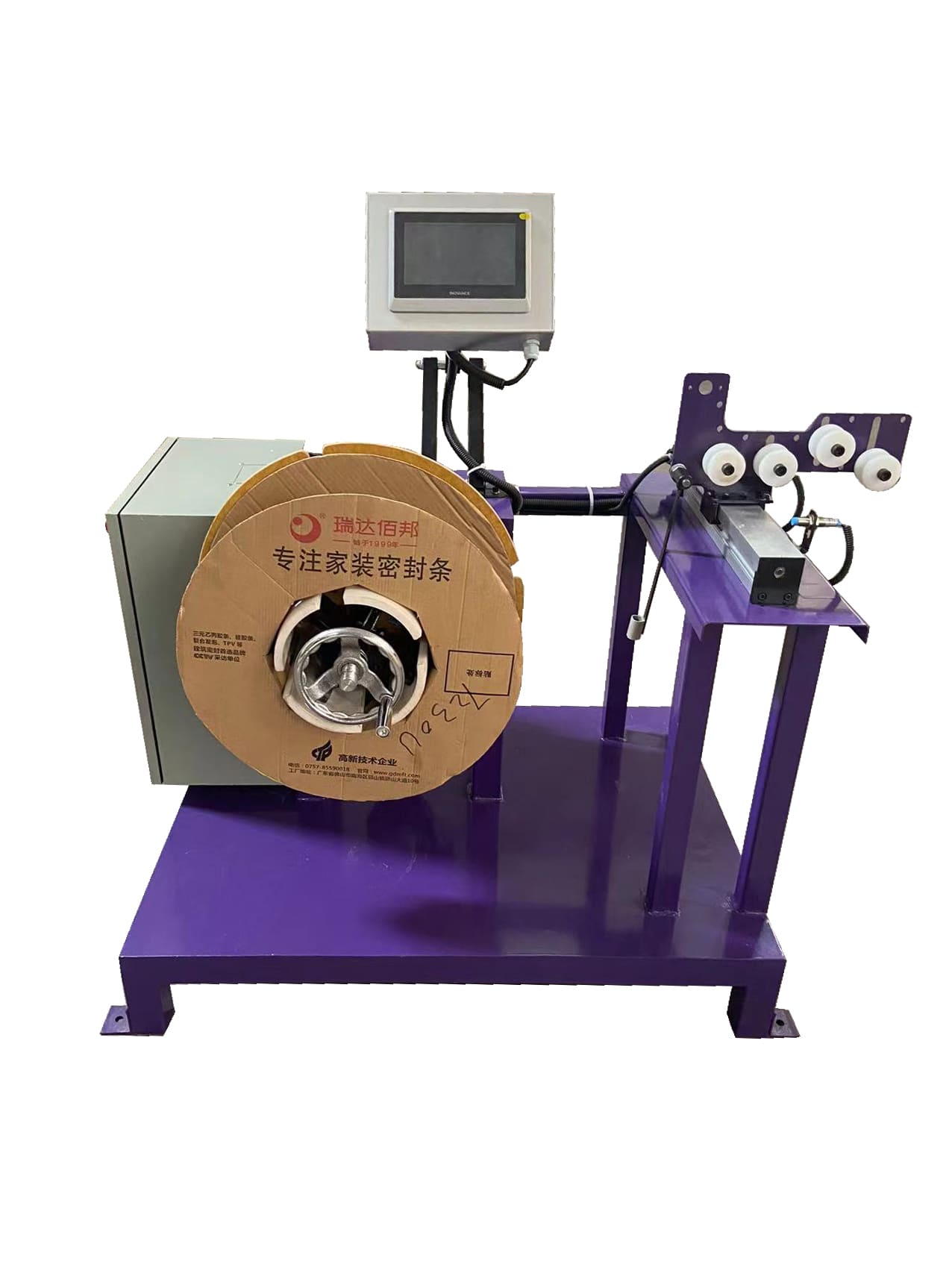
Automatic winding machines are designed to automate the process of winding materials such as wires, yarns, or films onto spools, bobbins, or other forms of packaging. This automation not only speeds up production but also ensures consistency and precision, which are critical in meeting the stringent quality standards of modern manufacturing.
Applications Across Industries
Electrical and Electronics Industry
In the electrical and electronics sector, automatic coil winding machines play a pivotal role in the production of transformers, motors, and other electrical components. These machines are capable of winding coils with high precision, ensuring uniformity in electrical and magnetic properties. This consistency is crucial for maintaining the performance and reliability of electrical devices. For instance, automated coil winding machines can handle a wide range of materials, including magnet wires and insulating tapes, allowing for continuous production without manual intervention.
Textile Industry
The textile industry has also seen significant benefits from automatic winding machines. These machines are used to wind yarn, thread, or fibers onto spools or cones, ensuring precision and uniformity in the winding process. This is essential for producing high-quality yarns that perform well in subsequent textile processes like weaving and knitting. Automatic winding machines reduce labor costs, minimize errors, and increase throughput, making them indispensable in modern textile manufacturing.
Wire and Cable Industry
In the wire and cable industry, automatic winding machines are used to wind various types of wires, such as AC, DC, and data lines. These machines offer versatility and can handle different wire types efficiently, ensuring consistent product quality and improving production efficiency.
Logistics and Packaging
Beyond manufacturing, automatic winding machines are also used in logistics and packaging. They help improve packaging efficiency by automatically handling, packaging, and securing materials, reducing labor costs, and enhancing overall productivity.
Medical and Pharmaceutical Industry
In the medical sector, automatic winding machines are utilized in the production of medical devices, such as suture and needle assemblies. These machines enable precise and efficient assembly processes, ensuring high-quality products that meet stringent medical standards.
Benefits of Automatic Winding Machines
The integration of automatic winding machines into manufacturing processes offers several key benefits:
Improved Productivity: Automated machines achieve significantly higher production rates compared to manual processes, reducing lead times and increasing output without sacrificing quality or precision.
Consistency and Repeatable Quality: Automation ensures consistent winding patterns, wire tension, and pitch, resulting in uniform products of superior quality. This consistency eliminates variations caused by human error, maintaining high standards throughout the production run.
Cost Savings: By reducing labor costs associated with manual winding, maximizing material utilization, and minimizing scrap, manufacturers can realize substantial cost savings.
Enhanced Safety: Automating hazardous tasks prioritizes worker safety and reduces the risk of accidents in the production environment.
Scalability and Adaptability: Automated systems are highly scalable, enabling manufacturers to meet growing demands without significant investments in additional workforce or machines. They can easily handle various product types and sizes, making them adaptable to changing production requirements.
Innovations and Future Prospects
Recent advancements in automatic winding machine technology have focused on enhancing versatility, efficiency, and safety. Modern machines are equipped with advanced features such as real-time monitoring, automatic fault detection, and precision control systems. These innovations have led to improved quality standards and increased productivity across industries.
As manufacturing continues to evolve, the role of automation will become even more central. The integration of technologies like AI and IoT into winding machines is expected to further enhance their capabilities, offering real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance. This will enable manufacturers to optimize production processes more effectively, reducing downtime and improving overall efficiency.
Moreover, the trend towards sustainability is driving the development of energy-efficient and waste-reducing winding machines. As industries prioritize environmental responsibility alongside productivity, automatic winding machines will play a crucial role in aligning manufacturing processes with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion
Automatic winding machines have become indispensable in modern manufacturing, offering a wide range of applications across diverse industries. Their ability to enhance productivity, ensure consistent quality, and reduce costs makes them a vital component of efficient production processes. As technology continues to advance, the future of automatic winding machines looks promising, with potential for further innovations that will drive manufacturing forward.
In conclusion, the applications of automatic winding machines in modern manufacturing are vast and varied, contributing significantly to the efficiency, quality, and sustainability of production processes. As industries continue to evolve and grow, the importance of these machines will only increase, making them a cornerstone of future manufacturing technologies.